
Anatomical structure of Monocot Stem:
T.S. of a monocot stem shows the following anatomical features:
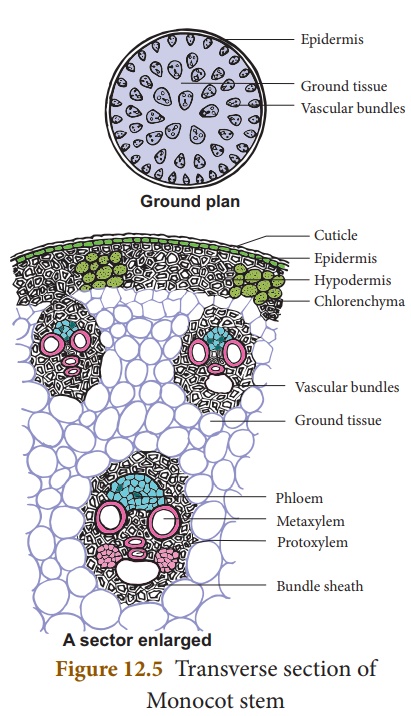
Epidermis:
- It is the single outermost layer composed of small, thin-walled, somewhat barrel-shaped parenchymatous cells which are tightly packed without intercellular species.
- It is externally covered with thick cuticle.
- A few stomata are present on epidermis.
- Usually trichomes or hairs are lacking.
Cortex:
- It lies below the epidermis.
- Cortex is composed of following regions:
- Hypodermis:
- It lies just below the epidermis.
- It comprises of 2-3 layers of thick-walled lignified sclerenchymatous cells, without intercellular spaces.
- It helps in mechanical support.
Ground tissue:
- It contains a continuous mass of thin-walled, round parenchymatous tissue which lies below the hypodermis.
- The intercellular spaces are present.
- Cells are rounded or polygonal in shape.
- There is no differentiation of general cortex, endodermis, pericycle, pith, and rays.
- Vascular bundles are irregularly lodged in this region.
Vascular bundles:
- Vascular bundles are irregularly scattered in the ground tissues, called atactostele.
- These are conjoint, collateral, and closed type.
- Vascular bundles occurring in the peripheral region are smaller in size and compactly arranged.
- In contrast, those occurring towards the central region are larger in size and widely placed.
- All the vascular bundles have similar structure.
- Each vascular bundle consists of xylem towards the center and phloem towards the periphery without cambium.
- It is oval in shape and surrounded by a sheath of sclerenchymatous tissue.
Xylem:
- It is V or Y shaped, bearing two large metaxylem vessels with wider cavities and pitted thickening at the lateral arms.
- Few tracheids are present in between the metaxylem vessels.
- Protoxylem vessels are only one or two, smaller, narrow cavities having annular or formed lysigenously by disintegrating by disintegration or breaking of some cells or parenchyma tissue and rarely protoxylem vessels.
- Thin-walled xylem parenchyma is present around the protoxylem vessels.
Phloem:
- It lies outside the xylem and is partly present near the metaxylem vessels.
- It is composed of sieve elements and companion cells.
- In a mature bundle, the protophloem gets crushed just below the sheath. So, the inner portion is meta-phloem.
- Sieve tubes appear polygonal in T.S. having internally situated companion cells.
- It conducts the organic food.
