Western blot
Principle:
- Western blotting technique is used for identification of particular protein from the mixture of protein.
- In this method labelled antibody against particular protein is used identify the desired protein, so it is a specific test. Western blotting is also known as immunoblotting because it uses antibodies to detect the protein.
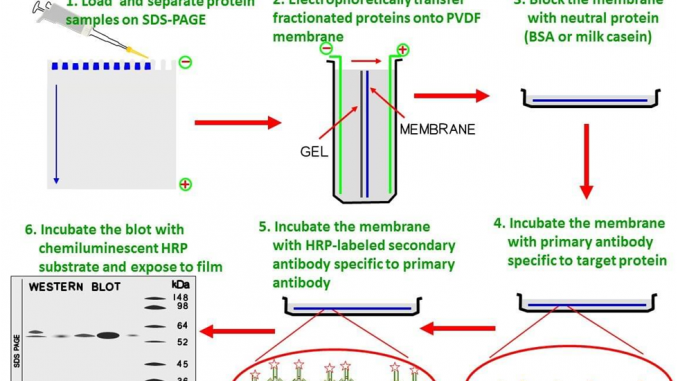
Procedure/Steps:
- Extraction of protein
- Gel electrophoresis: SDS PAGE
- Blotting: electrical or capillary blotting
- Blocking: BSA
- Treatment with primary antibody
- Treatment with secondary antibody( enzyme labelled anti Ab)
- Treatment with specific substrate; if enzyme is alkaline phosphatase, substrate is p-nitro phenyl phosphate which give color.
Step I: Extraction of Protein
- Cell lysate is most common sample for western blotting.
- Protein is extracted from cell by mechanical or chemical lysis of cell. This step is also known as tissue preparation.
- To prevent denaturing of protein protease inhibitor is used.
- The concentration of protein is determined by spectroscopy.
- When sufficient amount of protein sample is obtained, it is diluted in loading buffer containing glycerol which helps to sink the sample in well.
- Tracking dye (bromothymol blue) is also added in sample to monitor the movement of proteins.
Step II: Gel electrophoresis
- The sample is loaded in well of SDS-PAGE Sodium dodecyl sulfate- poly-acrylamide gel electrophoresis.
- The proteins are separated on the basis of electric charge, isoelectric point, molecular weight, or combination of these all.
- The small size protein moves faster than large size protein.
- Protein are negatively charged, so they move toward positive (anode) pole as electric current is applied.
Step III: Blotting
- The nitrocellulose membrane is placed on the gel. The separated protein from gel get transferred to nitrocellulose paper by capillary action. This type of blotting is time consuming and may take 1-2 days
- For fast and more efficient transfer of desired protein from the gel to nitrocellulose paper electro-blotting can be used.
- In electro-blotting nitrocellulose membrane is sandwich between gel and cassette of filter paper and then electric current is passed through the gel causing transfer of protein to the membrane.
Step IV: Blocking
- Blocking is very important step in western blotting.
- Antibodies are also protein so they are likely to bind the nitrocellulose paper. So before adding the primary antibody the membrane is non-specifically saturated or masked by using casein or Bovine serum albumin (BSA).
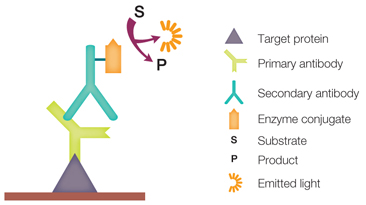
Step V: Treatment with Primary Antibody
- The primary antibody (1° Ab) is specific to desired protein so it form Ag-Ab complex
Step VI: Treatment with secondary antibody
- The secondary antibody is enzyme labelled. For eg. alkaline phosphatase or Horseradish peroxidase (HRP) is labelled with secondary antibody.
- Secondary antibody (2° Ab) is antibody against primary antibody (anti-antibody) so it can bind with Ag-Ab complex.
Step VII: Treatment with suitable substrate
- To visualize the enzyme action, the reaction mixture is incubated with specific substrate.
- The enzyme convert the substrate to give visible colored product, so band of color can be visualized in the membrane.
- Western blotting is also a quantitative test to determine the amount of protein in sample.
Application:
- To determine the size and amount of protein in given sample.
- Disease diagnosis: detects antibody against virus or bacteria in serum.
- Western blotting technique is the confirmatory test for HIV. It detects anti HIV antibody in patient’s serum.
- Useful to detect defective proteins. For eg Prions disease.
- Definitive test for Creutzfeldt-Jacob disease, Lyme disease, Hepatitis B and Herpes
