
- Vitamin C is well known for its ability to treat Scurvy.
- It is water soluble vitamin, also know as ascorbic acid.
- Vitamin C has three major roles:
- Firstly, it catalyzes the hydroxylation reactions especially prolyl and lysyl residues of collagen. Thus, promoting the formation of connective tissues and bones.
- Secondly, it actively participates in anti-oxidation. It is very powerful reductant.
- Thirdly, it helps in the absorption of iron from the intestine.
Properties of Ascorbic acid (Vitamin C):
- Ascorbic acid is a colourless and odourless crystalline substance.
- It is slightly sour in taste and optically active.
- Only the L-isomer has antiscorbutic properties.
- It is water-soluble and dissolves in alcohol too.
- It is not soulble in chloroform, solvent ether and light petroleum.
- It is readily oxidized, particularly in the presence of copper and iron but not of aluminium.
- It is for this reason that the foods cooked in copper utensils lose ascorbic acid quickly.
- This vitamin is also quickly deformed by alkalies.
- However, it is stable in weak acid solutions.
- This is why, baking soda shows a deleterious effect however, cooking in steam degrades very little amount of ascorbic acid.
- Loss of ascorbic acid occurs in case of drying of vegetables and their storage.
- Freezing has no harmful effect on this vitamin.
- Little loss of ascorbic acid occurs when citrus fruit juices and tomato juice are canned.
- Because of its easily oxidizable nature, the ascorbic acid is a powerful reducing agent.
Biosynthesis of Vitamin C:
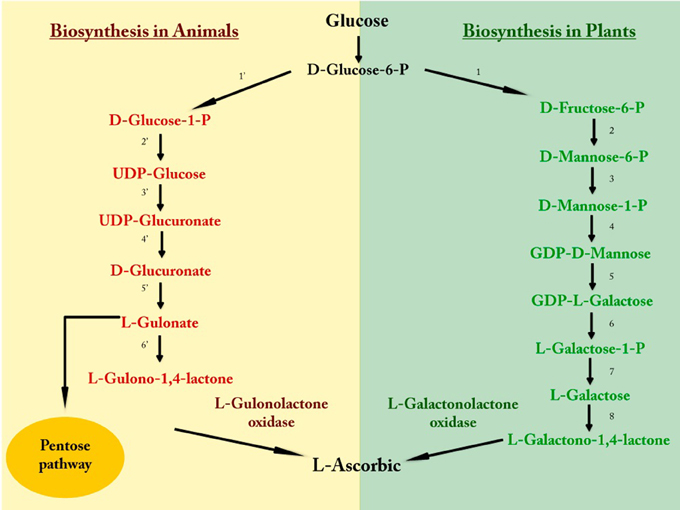
- Source of vitamin C is plants. However, many animals can synthesize ascorbic acid from glucose by uronic acid pathway.
- However, Human and other primates, guinea pigs and bats cannot synthesize ascorbic acid due to the deficiency of a single enzyme L-gulonolactoneoxidase.
- The enzyme L- gluconolactone oxidase is required to convert L-glucono-1,4-lactone into L-ascorbic acid in final step of the pathway.
Biological functions of Vitamin C:
- Collagen formation:
- Vitamin C catalyzes the post translational modification responsible for the hydroxylation of prolyl and lysyl residues of collagen fibres.
- Bone consists of high percentage of collagen and requires vitamin C for proper formation.
- Serotonin synthesis:
- Vitamin C is responsible for hydroxylation reaction involved in synthesis of serotonin from tryptophan.
- Folate metabolism:
- Dihydrofolate reductase (DHFR) requires Vitamin C for its activity.
- Therefore, Vitamin C has a role in synthesis of 5,10-methylene tetra hydro folate (THF) acid from7,8-dihydrofolate (DHF).
- Cholesterol synthesis:
- Enzyme 7-α-hydroxylase involved during cholesterol biosynthesis requires Vit.C.
- Haemoglobin synthesis:
- Vitamin C help absorption of iron from intestine which is required for hemoglobin synthesis.
- Steroid hormone synthesis:
- Vitamin C catalyses the hydroxylation reaction involved during the biosynthesis corticosteroid hormones.
- Adrenal gland and gonads:
- Vitamin C is required in excessive amount for proper maintenance and functioning of adrenal gland and gonads.
- Prevention of diseases:
- Vitamin C along with Vit-A and E delays the onset of cataract.
- Vitamin C has been associated for the prevention of coronary heart diseases and tumor formation along with Vit-A and E.
- Antioxidants:
- Vitamin C has a sparing action on Vitamin A and E and also some vit-B and prevent their oxidation.
- Vit-C prevent the oxidation of cellular components by the effect of free radicals, peroxides, superoxides etc.
- Immunological function:
- Vitamin C has been found to be involved in the stimulation of Antibody formation and enhancement of phagocytosis.
- Wound healing
Recommended daily allowance (RDA):
- Pregnant women, people involved in smoking, alcoholism, use of contraceptive devices require higher dose of Vitamin C.
- RDA varies from 60-70 mg/day.
Dietary sources of Vitamin C:
- Lemon, gooseberry (amala), guava, cabbage, tomatoes, potato skin, are good source of vitamin C.
- (Milk is not a good source)
Deficiency of Vitamin C:
- Vitamin C deficiency results in scurvy (a disease characterized by the spongy and sore gums, loose teeth), anemia, swollen joints and fragile blood vessel.
- Lack of adequate Vitamin C results in reduced immune-competence.
- Vitamin C deficiency also results in sluggish hormonal function of adrenal gland and gonads.
- Hemorrhage and osteoporosis are caused by deficiency of Vitamin C.
- Also, delayed wound healing occurs in deficiency of vitamin C.
Megadoses of vitamin C (Hypervitaminosis C):
- High doses of Vitamin C ,300-400 times exceeding the normal value(18gm) can be used in the treatment of common cold, trauma and prevention of onset of diseases such as cataract, coronary heart diseases, and onset of tumor.
