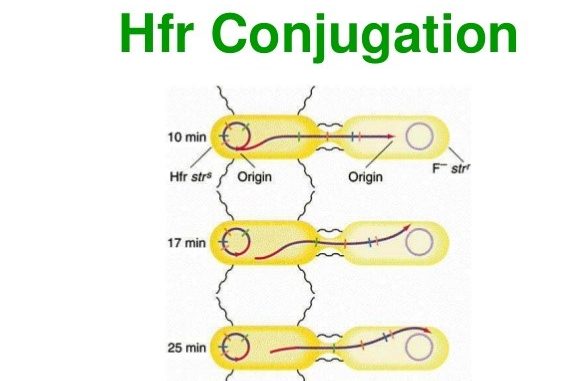
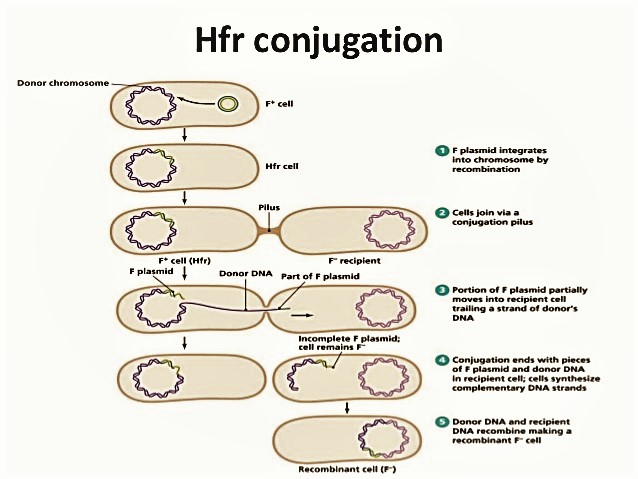
High frequency recombination (Hfr) cell conjugation and F-prime (F’) cell
Hfr cell
- When F-plasmid (sex factor) integrated with chromosomal DNA then such bacteria is known as high frequency recombination (Hfr) bacteria.
- In the cross (conjugation) between Hfr cell and F- cell, frequency of recombination is very high but frequency of transfer of whole F-factor is very low.
- Hfr cell acts as donor while F- cell acts as recipient.
- At first F-factor makes sex pilus that joins donor and recipient cell then F- factor opens as replication origin then one strand is cut down. Now the 5’ end of this strand enters into recipient cell through conjugation tube.
- Since, replication origin lies somewhere in the middle of F- factor, portion of F-factor that lies at 5’ end enters first into recipient cell but the portion situated at 3’ end enters only when whole chromosomal DNA enters into the recipient cell.
- To transfer whole chromosomal DNA, it takes 100 minutes in E. coli. In most of the cases, sex pilus (conjugation tube) breaks before transfer of whole chromosomal DNA takes place. So, frequency of transfer of whole F-factor is very low. After the cross between Hfr cell and F- cell, recipient cell remains recipient.
- In this conjugation, chromosomal DNA is always almost transfer from donor to recipient cell together with portion of F- factor. So, frequency of recombination is high.
F –prime (F’) cell:
- Bacteria in which contains F-factor and a part of chromosomal DNA integrated in it is known as F-prime bacteria.
F’ cells are formed from Hfr cell during induction of F- factor from chromosomal DNA in which F-factor carries a portion of chromosomal DNA along with it. - In the cross (conjugation) between F-prime (F’) cell and F- cell, frequency of recombination is high as well as frequency of transfer of whole F-factor is also high.
