Erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR): principle, method, procedure and clinical application
Principle of ESR:
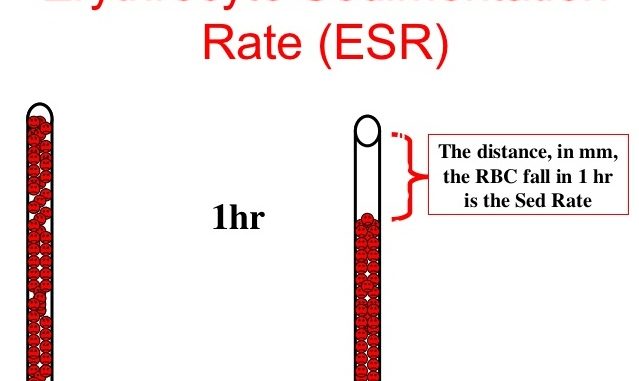
When an anticoagulant is added to the blood and this well mixed venous blood is placed in a vertical tube, erythrocytes tend to settle towards bottom leaving clear plasma on top. This rate of sedimentation of red blood cells in a given interval of time is called erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR).
As the erythrocytes sediments, in a period of one hours, 3 stages can be observed.
- Stage I: first 10 minutes
- It is initial period of aggregation during which rouleaux are formed and the sediment rate is low
- Stage II: next 4o minutes
- It is a period of fast setting. Sedimentation occurs at a constant rate during this period
- Stage III: next 10 minute or more
- The sedimentation again slows as it is the final period of packing of cells at the bottom of the tube
Factors affecting ESR:
- There are several factors that affects sedimentation of erythrocytes.
-
Factors that increases ESR:
- Anemia:
- anemia increase ESR because the change in erythrocyte-plasma ratio favors rouleaux formation.
- Rouleaux is aggregation of RBCs together due to their discoid shape.
- Rouleaux have a decrease surface area and accelerate ESR
- Increase level of fibrinogen:
- it decreases the negative charge of erythrocyte, so RBC tend to remain apart and this promotes formation of rouleaux and increase ESR
- Immunoglobulin:
- increase antibody level in blood increase ESR
- Increase cholesterol level
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Chronic infections
- Carcinoma
- Tissue destruction and other disease
- Anemia:
-
Factors that decrease ESR:
- Defibrinigenation:
- removal of fibrinogen decreases ESR
- Increase albumin and lecithin in blood
- Abnormal or sickle shape RBCs:
- abnormal or irregular shape of RBC lower ESR
- Congestive heart failure
- Defibrinigenation:
Method for ESR estimation:
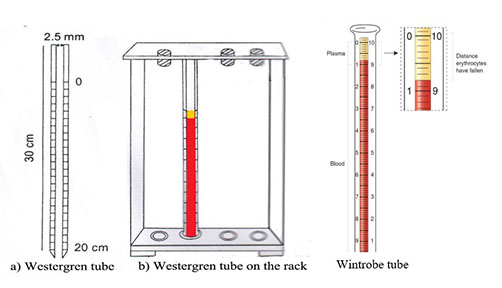
Westergren method for ESR estimation is widely used method. Wintrobe method is also used for ESR determination. Wintrobe tube is smaller than westergren tube
Materials required:
- Westergren tube or wintrobe tube
- Anticoagulant: 0.1 M sodium citrate
- ** in modified westergren method EDTA is used as anticoagulant
Procedure for ESR estimation:
- Withdraw 4 ml of venous blood
- Mix exact 10ml of sodium citrate with 4ml of venous blood in a tube
- Invert the tube 2-3 times to mix the blood thoroughly with anticoagulant
- Fill the westergren tube up to mark 0 and place in the rack at room temperature undisturbed and away from sunlight.
- Take the reading exactly after 1 hour. Record in millimeters from top surface of column to top of RBC sediments.
Result:
- Normal value of ESR
- Female:
- under 50 years- 20 mm/hr
- above 50 years- 30mm/hr
- Male:
- Under 50 years- 15mm/hr
- Above 50 years- 20 mm/hr
- Female:
Clinical application of ESR estimation:
- ESR test is non-specific test although it is used as indication of presence of disease
- ESR value increase during rheumatoid arthritis, chronic infection, carcinoma, tissue destruction and nephritis
- During pregnancy, ESR increase moderately from 10th or 12th weeks onwards and return to normal after delivery.
- ESR value decreases in sickle cell anemia and congestive heart failure (CHF).
