Catalase test
Objective:
- to check whether the tested microorganisms (bacteria) is aerobic or anaerobic
Principle:
Catalase is an enzyme that breaks Hydrogen peroxide (H2O2), a toxic metabolic byproducts of aerobic and facultative anaerobic bacteria into non toxic products water (H2O) and Oxygen (O2). H2O2 is toxic to cells. It is highly reactive molecule that damage cell components. So the bacteria living in presence of Oxygen produces enzyme catalase that breakdown H2O2 into H2O and O2
H2O2 ————catalase—–>H2O + O2
Catalase is an inevitable enzyme for the aerobic organisms. Hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) is produced as the result of non-enzymatic transfer of electrons from reduced flavoprotein to Oxygen as well as by the action of superoxide dismutase. The enzyme catalase degrades hydrogen peroxide in cell before it can do any damage to cell. Aerobic and facultative anaerobes have catalase enzyme to convert H2O2 into non toxic forms while obligate anaerobes so not have such enzyme, therefore they cannot tolerate O2.
FP H2( reduced flavoprotein) + O2—————->FP (oxidized flavoprotein)+ H2O2
2H+ + 2 O2– ——————–> H2O2 + O2
Most microorganisms that are aerobic and facultative anaerobic produce the enzyme catalase except Streptococcus spp, lactobacillus spp, Leuconostoc spp, Clostridium spp, Mycoplasma. Other bacteria that do not produce catalase enzyme are Obligate anaerobes or microaerophiles. Absence of enzyme catalase is the reason why oxygen is poisonous to anaerobes.
Application: Catalase test is carried out to differentiate the genus Staphylocaccus spp which give positive test from genus Streptococcus spp which give negative test.
Requirements:
- Culture of Staphylococcus spp and Streptococcus spp
- 3% Hydrogen peroxide
- A glass slide, test tubes
- Glass rod
Procedure:
Slide test:
- Prepare a fresh Hydrogen peroxide 3% solution
- Place a drop of 3% H2O2 on opposite ends of a clean grease free glass slide with the help of dropper
- Transfer as small portion of both cultures onto drop of 3% H2O2 with the help of a sterile glass rod.
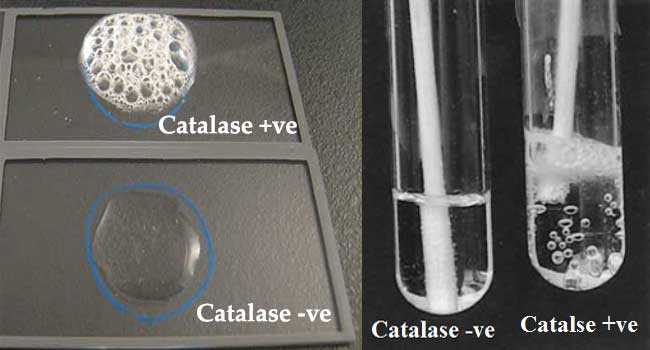
- Examine for immediate bubbling effervescence of O2
*note: slide test is not recommended because of risk of contamination from active bubbling
Tube test:
- Pour 2-3 ml of 3% Hydrogen peroxide into a test tube
- Transfer the culture with the help of glass rod and immense into H2O2 solution
- Observe for immediate effervescence or bubbling
Result:
- Staphylococcus spp: give effervescence of gas, Catalase Positive
- Streptococcus spp: give No effervescence of gas, catalase Negative

Precautions:
- Do not use wire loop to transfer the culture as H2O2 may reacts with iron or nichrome to give false result
- H2O2 is toxic to human, so handle carefully
- Observe the result within 30 seconds
- Culture should not be more than 24 hours old
Reference:
- Manandhar S, Sharma S (2006), “ practical approach to Microbiology”
- Cheesbrough M (1989), “medical laboratory manual for tropical countries”
