RPR test: Principle, Procedure, Result interpretation and Application
Principle:
- RPR test stands for Rapid Plasma Regain test. It is a serological test used for the diagnosis of syphilis. Syphilis is a sexually transmitted diseases caused by Treponema pallidum. RPR test looks for the autoantibodies that reacts with cardiolipin antigen. Cardiolipin antigen is a component of mitochondrial membrane of host cell released due to tissue damage caused by T. pallidum. In response to cardiolipin autoantibodies are produced in the body. However, in other infection and diseases such as other treponemal infection, occasionally during pregnancy, in acute malaria, leprosy, tuberculosis, viral pneumonia, leptospirosis, cancer, infectious mononucleosis, and sometimes after certain vaccination autoantibodies are produced.
- RPR is similar to VDRL test but the cardiolipin antigen particle are either carbon coated or dyed to enable the reaction to read macroscopically. RPR test is also known as modified VDRL test.
- In RPR test, heating of serum is not required. Furthermore both plasma and serum can be tested using RPR test. Antigen reagents is available commercially as ready to used, it does not require prior dilution. The unopened antigen has shelf-life of 1 year but storage at 2-6°C is recommended.
Reagents
- RPR antigen suspension:
- RPR antigen suspension is a stabilized combination of 0.003% cardiolipin, 0.020-0.022% lecithin, 0.09% cholesterol, 10% choline chloride, 0.0125M EDTA, 0.01875% charcoal, 0.01M Na2HP04, 0.01M KH2P04, 0.1% thimerosal in distilled water
- The antigen suspension is packaged in ampules. Store unopened ampules at 2° to 8°C; do not store the antigen in bright sunlight or in temperatures above 29°C; do not freeze. An unopened ampule of antigen is stable up to the expiration date.
- Control serum samples:
- Control serum samples are lyophilized reactive (R), minimally reactive (Rm), and nonreactive (N) control serum specimens on a card, or liquid or lyophilized serum samples of graded reactivity.
- If quantitative tests are to be performed, a control serum that can be titered to at least a 1:4 dilution should be used.
- *Store control cards or serum samples according to the manufacturer’s directions
- 0.9% Saline.
- Diluent (control):
- Prepare a 2% solution of human serum in 0.9% saline, by diluting a human serum nonreactive for syphilis 1:50 in 0.9% saline
Procedure:
- Bring the RPR test kit to room temperature.
- Add a measured volume of clear unhemolysed serum or plasma on marked area on card and also add a measured drop of antigen reagent.
- Rotate the card for 8 minutes to mix the content. (* a mechanical rotator is needed for those RPR test kits which require rotation for 8 minutes at a required speed and rotation diameter).
- Observe macroscopically and report the test reactive or non-reactive
- Reactive result shows clumping
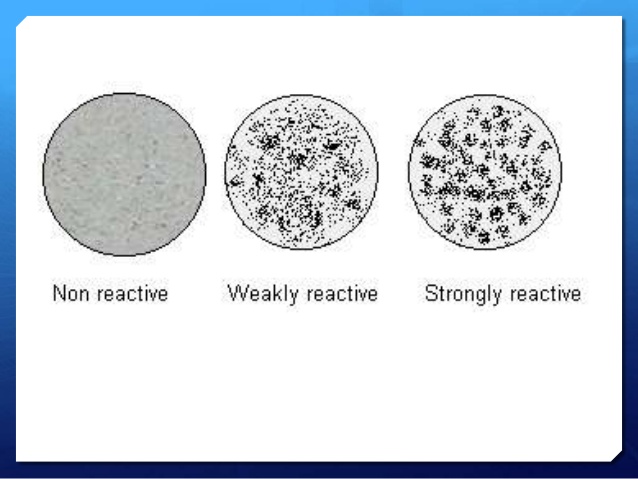
Result interpretation:
- Reactive (Positive): antigen-antibody clumping
- Non-reactive (Negative): even suspension of particles

RPR test positive (reactive) for
- Person infected with T. pallidum without symptoms.
- Other treponemal infection
- occasionally during pregnancy
- In acute malaria
- Leprosy
- Tuberculosis
- Viral pneumonia
- Leptospirosis
- Cancer
- Infectious mononucleosis
- Sometimes after certain vaccination.
Applications:
- It is card test because it is performed in commercially available card.
- Rapid and cost effective test
- Result can be visualized macroscopically
- More sensitive than VDRL
- Non treponemal test
- Screening test for syphilis
