
Pentose phosphate pathway (PPP) or Hexose mono-phosphate (HMP) shunt
• Pentose phosphate pathway is an alternative pathway to glycolysis and TCA cycle for oxidation of glucose.
• It is a shunt of glycolysis
• It is also known as hexose monophosphate (HMP) shunt or phosphogluconate pathway.
• It occurs in cytoplasm of both prokaryotes and eukaryotes
• Pentose phosphate pathway starts with glucose and it is a multi-steps reaction.
• The sequence of reactions are divided into two types.
I) oxidative reaction phase
II) Non-oxidative reaction phase
Oxidative phase: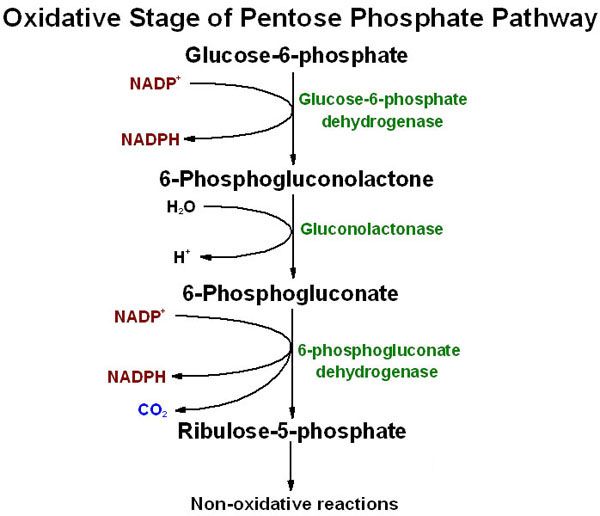
- First four reactions are irreversible and oxidative in which glucose molecule is oxidized twice generating two molecules of NADPH and glucose is converted into Ribose-5 phosphate.
1st reaction: conversion of glucose to glucose-6 phosphate.
- This reaction is catalyzed by the enzyme hexokinase and a molecule of ATP is utilized. This reaction is actually a primary step of glycolysis.
2nd reaction: conversion of glucose-6 phosphate to 6-phosphogluconolactone.
- This reaction is catalyzed by an enzyme glucose-6 phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD) in the presence of Mg++ ion.
- In this reaction a molecule of NADPH is produced.
3rd reaction: conversion of 6-phosphogluconolactone to 6-phosphogluconate
- This reaction is a hydrolysis reaction catalyzed by hydrolase enzyme
4th reaction: conversion of 6-phosphogluconate to ribose-5 phosphate
- This reaction is catalyzed by the enzyme 6-phosphogluconate dehydrogenase to produce 3-keto-6-phosphogluconate which undergoes decarboxylation to produce ribulose-5 phosphate.
- In this reaction a molecule of NADPH is generated.
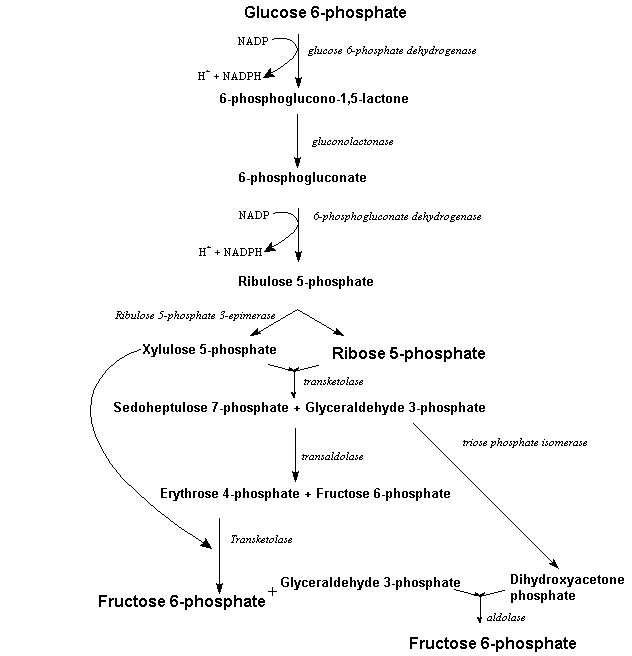
Non oxidative phase: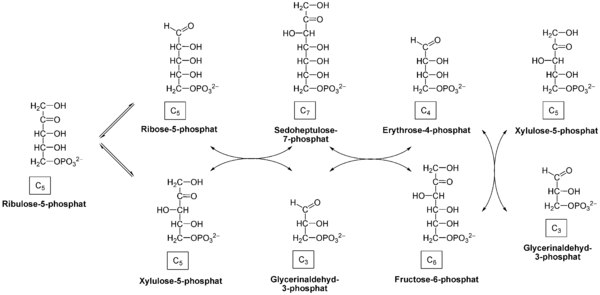
- Oxidative reactions is followed by a series reversible sugar phosphate inter-conversion reaction.
- Ribulose-5-phosphate is epimerized to produce xylulose 5-phosphate in the presence of enzyme phosphor pentose epimerase. Similarly ribulose-5-phosphate is also keto-isomerized into ribose 5-phosphate.
- Xylulose-5-phsphate transfer two carbon moiety to ribose 5-phospahate in the presence of enzyme transketolase to form sedoheptulose-7-phosphate and glyceraldehyde 3—phosphate.
- Sedoheptulose -7-phosphate transfer three carbon moiety to glyceraldehyde -3-phosphate to form fructose 6-phopsphate and erythrose 4-phosphate in the presence of enzyme transaldolase.
- Transketolase enzyme catalyse the transfer of two carbon moiety from Xylulose-5-phsphate to erythrose-4- phosphate to form fructose-6-phosphate and glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate.
- Fructose-6-phosphate and glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate is later enter into glycolysis and kreb’s cycle.
- The rate and direction of reversible reaction depends upon the needs of cell.
- If cell needs only NADPH then fructose-phosphate and glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate are converted back to glucose by reverse glycolysis, otherwise converted to pyruvate and enter TCA cycle generating ATPs.
Significance of Pentose phosphate pathway
- HMP is only the cytoplasmic pathway that generates NADPH
- NADPH is produced in this pathway acts as reducing agent during biosynthesis of various molecules eg. fattyacids.
- This pathway generates 3, 4, 5, 6 and 7 carbon compounds which are precursors for biosynthesis of other molecules. Eg nucleotides are synthesized from ribose-5-phsophate.
- Pentose phosphate pathway is very essential for cell lacking mitochondria (eg.RBCs) for generation of NADPH.
- Triose, tetrose, pentose, hexose and heptose sugar are generated as intermediate products in pentose phosphate pathway.
- NADPH is also used to reduce (detoxify) Hydrogen peroxide in cell.
- Resistance to malaria in some Africans are associated with deficiency of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase enzyme because malarial parasites depend upon HMP shunt to reduce glutathione in RBCs.
