Major histocompatibility complex (MHC): structure, types and functions
- Major histocompatibility complex (MHC) is the cluster of gene arranged within a long continuous stretch of DNA on chromosome number 6 in Human which encodes MHC molecules.
- MHC molecule is a cell surface glycoprotein receptor present in APCs and acts as antigen presenting structure It plays vital role in immune recognition, including interaction between T cells and other cell types.
- In Human MHC is known as Human Leucocyte antigen (HLA) complex and the genes of MHC are recognized in three classes, consequently there are three types of MHC molecules.
Types of MHC:
- Class I MHC
- Class II MHC
- Class III MHC
|
HLA complex |
||||||||
| MHC class | MHC I | MHC II | MHC III | |||||
| Region | A | B | C | DP | DQ | DR | C4, C2, BF | |
| Gene products | HLA-A | HLA-B | HLA-C | DP, αβ | DQ, αβ | DR, αβ | C’ Protein | TNF-α TNF-β |
MHC class-I:
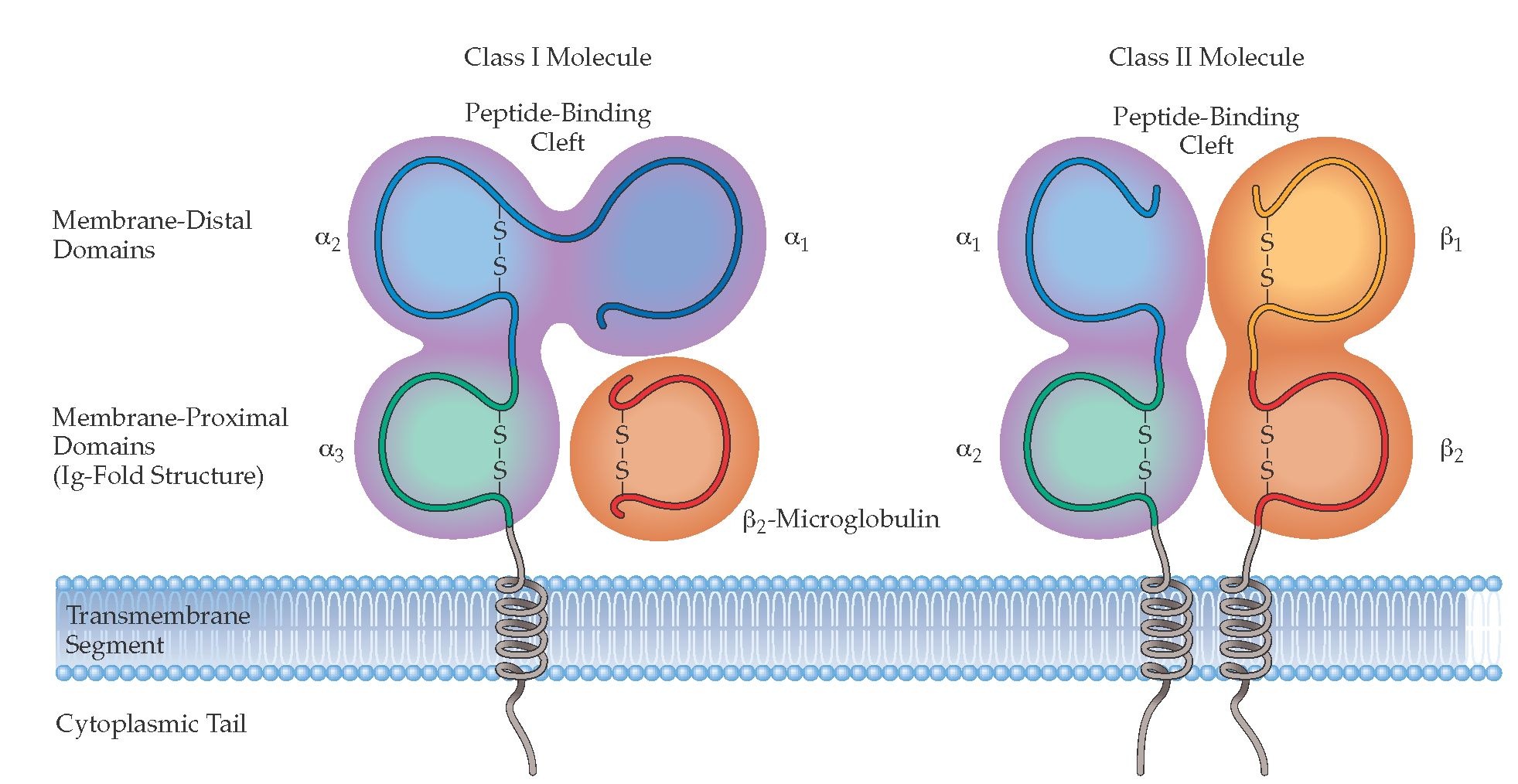
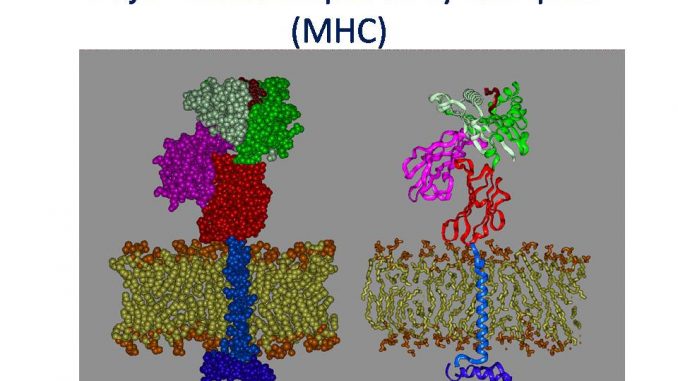
- Class-I MHC gene encodes glycoprotein molecule which expressed on the surface of all nucleated cells and platelets.
- MHC-I molecule contains a 45KDa α-chain associated non-covalentely with a 12KDa β2 microglobulin molecule.
- Association of α-chain and β2 microglobulin is required for expression of class-I MHC molecule on cell membrane.
α-chain of MHC-I:
- The α-chain is a transmembrane glycoprotein encoded by polymorphic gene within A, B and C region of Human HLA complex
- The α-chain is anchored in the plasma membrane by its hydrophobic trans-membrane segment and hydrophilic cytoplasmic tail.
- α-chain is made up of 3 domains (α1,α2 and α3). Each domain containing approximately 90 aminoacids, a transmsmbrane domain of about 25 hydrophobic aminoacids followed by short stretch of charged (hydrophilic) aminoacids of cytoplasmic tails of 3o aminoacids.
- α1 and α2 domains interacts to form a deep groove on the top which is a peptide binding clift. It can binds antigen of 8-10 animoacids long.
- α3 and β2 are organized into β-pleated sheets, each formed by antiparallel β-strand of aminoacids, this structure is known as immunoglobulin fold. Because of this structure α-chain and β2 microglobulin are classified as member of immunoglobulin super-family receptor.
β2 microglobulin of MHC-I:
- β2 microglobulin is a protein encoded by a highly conserved gene located on different chromosome
- β2 microglobulin is similar in size and organization to α3 domain.
- Β2 microglobulin does not contain transmembrane region and is non-covalently linked with α-chain.
Functions of MHC class I:
- Major function of MHC-I is to bind peptide antigens and present to CD8+ T cells (T helper cells)
- CD8 T cells are specific for MHC-I antigen
- MHC-I binds endogenous antigen and present to T helper cells.
- MHC-I molecules are found on surface of all nucleated cells.
MHC class-II:
- Class-II MHC is the glycoprotein molecule expressed primarily on antigen presenting cells such as macrophages, dendritic cells and B-cells.
- MHC-II molecules contains two different polypeptide chains, 1 33 KDa α-chain and 28KDa β-chain which are associated by non-covalent interactions.
α-chain and β-chain of MHC-II:
- α-chain and β-chain of MHC-II is a membrane bound glycoprotein that contains external domains, atransmembrane segment and acytoplasmic tail.
- α-chain and β-chain are made up of two domains (α1 and α2) and (β1 and β2) respectively.
- The peptide biding cleft is a open ended groove formed between α-chain and β-chain at proximal end. The cleft can bind antigenic peptide of 13-18 aminoacids long.
Functions of MHC class II:
- Major function of MHC-II is to bind peptide antigen and present to CD4 T cells.
- MHC-II are found on surface of Antigen presenting cells (APCs).
- CD4+T-cells are specific for MHC-II
- Activates B cells for antibody production
- MHC-II plays a significant role in graft versus host response and in mixed lymphocyte reaction (MLR) because the immune response gene is identical to MHC-II in human.
MHC class-III:
- MHc-III are diverse group of molecules that serves a wide variety of functions in immune system.
- MHC-III are not a marker on cell surface.
Functions of MHC class-III:
- Involved in complement activation
- Involved in inflammation caused by cytokines, tumor necrosis factors etc